Abstract
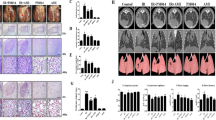
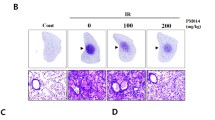
The aim of the study was to investigate the role of genistein in alleviating radiation-induced pneumonitis (RIP) through down-regulating levels of the inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting the expression of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox factor-1 (Ape1/Ref-1). Fifty female C57BL/6J mice (8 weeks old) were randomly divided into a control group, a pure irradiation (IR) group and a genistein + IR group. At the four time points after IR, hematoxylin, and Masson’s trichrome stainings were used to examine the pathological changes and collagen fiber deposition. Flow cytometry was used to detect reactive oxygen system (ROS) changes, EMSA was used to estimate the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) transcriptional activities and an ELISA assay was used to measure the levels of TGF-β1, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 in the serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) 2 weeks after IR. The pathological detection results showed acute inflammatory/fibrinoid exudation of the thoracic tissue after IR, which was significantly alleviated with genistein. The IR-induced an APE1 protein expression increase and NF-κB was effectively suppressed by genistein (P < 0.05). The induction of the inflammatory cytokines TGF-β1, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 by IR were in turn inhibited in the serum and BALF of the genistein-pretreated mice (P < 0.05). In addition, the ROS production was significantly boosted in the A549 cells after IR, which could be down-regulated by the pretreatment of genistein. The results demonstrate that genistein alleviates RIP by attenuating the inflammatory response in the initiation of RIP. A possible target of genistein is the Ape1/ref-1, which regulates key inflammatory cytokines by activating the NF-κB.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hosseinimehr, S. J. (2007). Trends in the development of radioprotective agents. Drug Discovery Today, 12, 794–805.
Rubin, P., Finkelstein, J., & Shapiro, D. (1992). Molecular biology mechanisms in the radiation induction of pulmonary injury syndromes: Interrelationship between the alveolar macrophage and the septal fibroblast. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 24, 93–101.
Beinert, T., Binder, D., Stuschke, M., Jorres, R. A., Oehm, C., Fleischhacker, M., et al. (1999). Oxidant-induced lung injury in anticancer therapy. European Journal of Medical Research, 4, 43–53.
Arpin, D., Perol, D., Blay, J. Y., Falchero, L., Claude, L., Vuillermoz-Blas, S., et al. (2005). Early variations of circulating interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels during thoracic radiotherapy are predictive for radiation pneumonitis. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 23, 8748–8756.
Chen, Y., Hyrien, O., Williams, J., Okunieff, P., Smudzin, T., & Rubin, P. (2005). Interleukin (IL)-1A and IL-6: Applications to the predictive diagnostic testing of radiation pneumonitis. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 62, 260–266.
Haase, M. G., Klawitter, A., Geyer, P., Alheit, H., Baumann, M., Kriegel, T. M., et al. (2003). Sustained elevation of NF-kappaB DNA binding activity in radiation-induced lung damage in rats. International Journal of Radiation Biology, 79, 863–877.
Linard, C., Marquette, C., Mathieu, J., Pennequin, A., Clarencon, D., & Mathe, D. (2004). Acute induction of inflammatory cytokine expression after gamma-irradiation in the rat: Effect of an NF-kappaB inhibitor. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 58, 427–434.
Ando, K., Hirao, S., Kabe, Y., Ogura, Y., Sato, I., Yamaguchi, Y., et al. (2008). A new APE1/Ref-1-dependent pathway leading to reduction of NF-kappaB and AP-1, and activation of their DNA-binding activity. Nucleic Acids Research, 36, 4327–4336.
Raffoul, J. J., Banerjee, S., Singh-Gupta, V., Knoll, Z. E., Fite, A., Zhang, H., et al. (2007). Down-regulation of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox factor-1 expression by soy isoflavones enhances prostate cancer radiotherapy in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Research, 67, 2141–2149.
Zhou, Y., & Mi, M. T. (2005). Genistein stimulates hematopoiesis and increases survival in irradiated mice. Journal of Radiation Research, 46, 425–433.
Messina, M. J., & Loprinzi, C. L. (2001). Soy for breast cancer survivors: A critical review of the literature. Journal of Nutrition, 131, 3095S–3108S.
Day, R. M., Barshishat-Kupper, M., Mog, S. R., McCart, E. A., Prasanna, P. G., Davis, T. A., et al. (2008). Genistein protects against biomarkers of delayed lung sequelae in mice surviving high-dose total body irradiation. Journal of Radiation Research, 49, 361–372.
Calveley, V. L., Khan, M. A., Yeung, I. W., Vandyk, J., & Hill, R. P. (2005). Partial volume rat lung irradiation: Temporal fluctuations of in-field and out-of-field DNA damage and inflammatory cytokines following irradiation. International Journal of Radiation Biology, 81, 887–899.
Ghafoori, P., Marks, L. B., Vujaskovic, Z., & Kelsey, C. R. (2008). Radiation-induced lung injury. Assessment, management, and prevention. Oncology, 22, 37–47. discussion 52–53.
Milano, M. T., Constine, L. S., & Okunieff, P. (2007). Normal tissue tolerance dose metrics for radiation therapy of major organs. Seminars in Radiation Oncology, 17(2), 131–140.
Travis, E. L., & De Luca, A. M. (1985). Protection of mouse lung by WR-2721 after fractionated doses of irradiation. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 11, 521–526.
Williams, J. P., Brown, S. L., Georges, G. E., Hauer-Jensen, M., Hill, R. P., Huser, A. K., et al. (2010). Animal models for medical countermeasures to radiation exposure. Radiation Research, 173, 557–578.
Wang, S., Liao, Z., Wei, X., Liu, H. H., Tucker, S. L., Hu, C. S., et al. (2006). Analysis of clinical and dosimetric factors associated with treatment-related pneumonitis (TRP) in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with concurrent chemotherapy and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT). International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 66, 1399–1407.
Hart, J. P., Broadwater, G., Rabbani, Z., Moeller, B. J., Clough, R., Huang, D., et al. (2005). Cytokine profiling for prediction of symptomatic radiation-induced lung injury. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 63, 1448–1454.
Johnston, C. J., Piedboeuf, B., Rubin, P., Williams, J. P., Baggs, R., & Finkelstein, J. N. (1996). Early and persistent alterations in the expression of interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA levels in fibrosis-resistant and sensitive mice after thoracic irradiation. Radiation Research, 145, 762–767.
Rube, C. E., Uthe, D., Schmid, K. W., Richter, K. D., Wessel, J., Schuck, A., et al. (2000). Dose-dependent induction of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in the lung tissue of fibrosis-prone mice after thoracic irradiation. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 47, 1033–1042.
Sont, J. K., De Boer, W. I., van Schadewijk, W. A., Grunberg, K., van Krieken, J. H., Hiemstra, P. S., et al. (2003). Fully automated assessment of inflammatory cell counts and cytokine expression in bronchial tissue. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 167, 1496–1503.
Ullmann, K., Wiencierz, A. M., Muller, C., Thierbach, R., Steege, A., Toyokuni, S., et al. (2008). A high-throughput reporter gene assay to prove the ability of natural compounds to modulate glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase and catalase gene promoters in V79 cells. Free Radical Research, 42, 746–753.
Zavodnik, L. B., Shkodich, A. P., Wielanek, M., Egorov, A. I., Zavodnik, I. B., Popov, Iu V, et al. (2006). Antioxidative effects of isoflavon genisteine-8-C-glycoside in vitro and in vivo. Eksperimental’naya i Klinicheskaya Farmakologiya, 69, 48–52.
Sarkar, F. H., & Li, Y. (2002). Mechanisms of cancer chemoprevention by soy isoflavone genistein. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 21, 265–280.
Evans, A. R., Limp-Foster, M., & Kelley, M. R. (2000). Going APE over ref-1. Mutation Research, 461, 83–108.
Acknowledgments:
We thank Ms. Yu-Xin Yang, and Ms. Ling Liao for their kind and excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30970865, 81272499, 81101783), National Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (CSTC2010BB5030) and Initial Fund for Returnees of Third Military Medical University (2009XHG17) to Prof. Zhen-Zhou Yang and Military Twelfth Five Key Projects (BWS11J038) to Guo-Dong Liu.
Disclosures
There is no any conflict of interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Guo-Dong Liu and Lei Xia contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, GD., Xia, L., Zhu, JW. et al. Genistein Alleviates Radiation-Induced Pneumonitis by Depressing Ape1/Ref-1 Expression to Down-regulate Inflammatory Cytokines. Cell Biochem Biophys 69, 725–733 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-9859-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-9859-x